How to operate a drone introduces the exciting world of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). This guide delves into the essential skills and knowledge needed to safely and effectively pilot a drone, from pre-flight checks and understanding controls to mastering basic flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial photography. We’ll cover everything from legal considerations and troubleshooting common issues to maximizing battery life and practicing safe flight techniques.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge, and a great resource for learning is available at how to operate a drone. This comprehensive guide will help you confidently take to the skies and operate your drone safely and effectively. Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to all relevant laws.
This exploration covers a wide range of topics, including detailed pre-flight checklists, safe operating procedures, mastering drone controls, executing smooth takeoffs and landings, performing basic flight maneuvers, and capturing breathtaking aerial imagery. We’ll also examine crucial aspects such as battery management, legal regulations, and effective troubleshooting strategies. By the end, you’ll possess the practical knowledge and confidence to operate your drone safely and creatively.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, checking weather conditions, and understanding emergency procedures. Adhering to safe operating distances is equally vital for preventing accidents and protecting both people and property.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection helps identify potential issues before they lead to accidents. The following table Artikels key components and their acceptable/unacceptable conditions:
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Condition, Securely Attached | No cracks, chips, or damage; firmly attached to motors | Cracks, chips, or significant wear; loose or damaged |
| Motors | Rotation, Sound | Smooth rotation, minimal vibration or unusual sounds | Rough rotation, excessive vibration, grinding sounds |
| Battery | Charge Level, Physical Condition | Sufficient charge (check your drone’s manual for recommended levels); no visible damage or swelling | Low charge; physical damage, swelling, or leakage |
| GPS | Signal Strength, Accuracy | Strong signal, accurate location | Weak or no signal; inaccurate location |
| Camera | Lens, Gimbal | Clean lens, gimbal moves smoothly | Dirty or scratched lens; gimbal jerky or unresponsive |
Weather Conditions, How to operate a drone
Adverse weather conditions can significantly impact drone flight safety. Strong winds, heavy rain, snow, or fog can reduce visibility and control, leading to accidents. Examples of unacceptable weather include wind speeds exceeding the drone’s specified limits (usually found in the drone’s manual), heavy precipitation obscuring visibility, and thunderstorms.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing what to do in case of emergencies is crucial. If the drone loses signal, immediately attempt to regain connection. If unsuccessful, initiate the return-to-home (RTH) function (if available). If the drone malfunctions, try to bring it down safely by gently lowering it to the ground. If the drone is uncontrollable, prioritize the safety of people and property.
Safe Operating Distances
Maintain a safe distance from people and obstacles. Avoid flying over crowds or near sensitive areas. The minimum safe distance varies depending on regulations and drone type, but always err on the side of caution. Consult local regulations and your drone’s manual for specific guidelines.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Mastering drone controls and understanding flight modes are essential for safe and effective operation. This section will guide you through calibrating controls, exploring different flight modes, and comparing control methods.
Controller Calibration
Before your first flight, calibrate your drone’s controls. This ensures accurate response and prevents unexpected movements. Most drones have a built-in calibration process, usually accessed through the drone’s app or controller. Follow the instructions provided in your drone’s manual. This typically involves placing the drone on a level surface and following on-screen prompts to center the sticks and sensors.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, providing a gentler learning curve. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots. GPS mode uses satellite data for positioning, enabling features like return-to-home. Attitude mode maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of its position in space.
Consult your drone’s manual for specific mode descriptions.
Joystick vs. App Controls
Joysticks offer precise, tactile control, preferred by many experienced pilots. App-based controls, while convenient, can be less precise, especially for complex maneuvers. The best choice depends on personal preference and experience. App controls are often simpler for beginners, while joysticks allow for finer control once proficiency is developed.
Drone Controller Functions

Understanding the functions of each button and switch on your drone controller is crucial. The specific layout varies between models, but common controls include:
| Button/Switch | Function |
|---|---|
| Left Joystick | Controls drone yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude) |
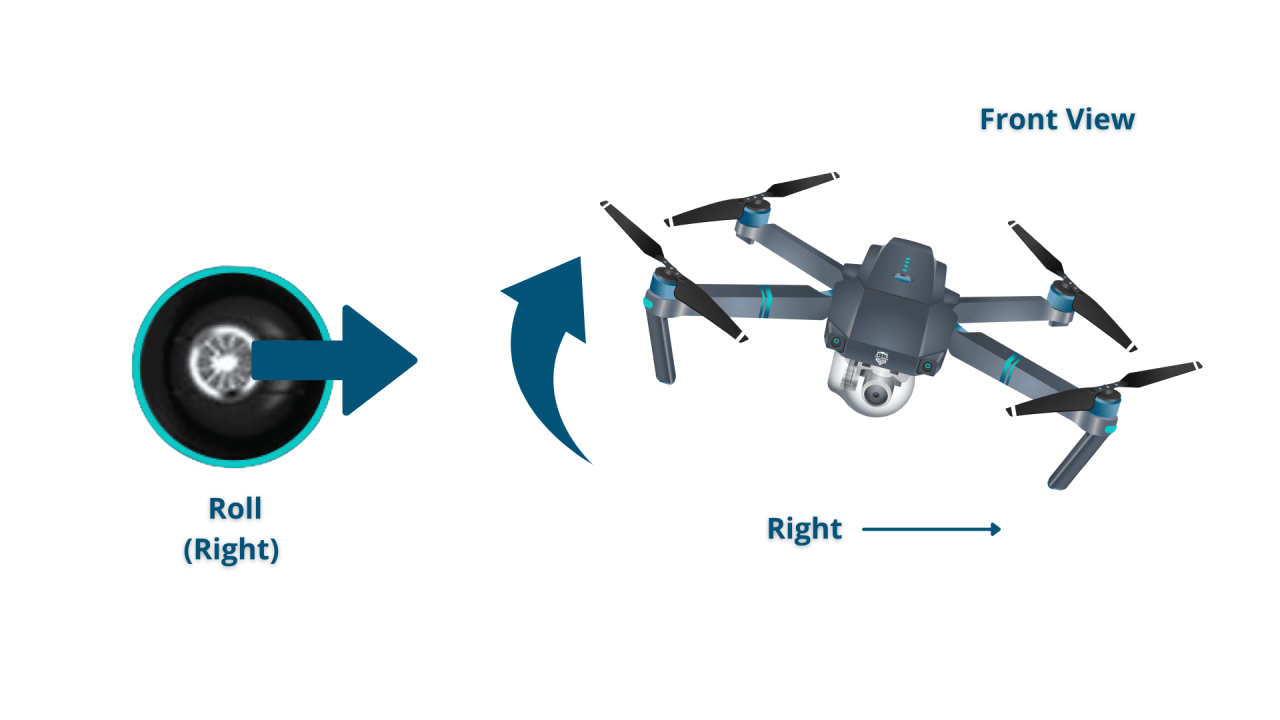
| Right Joystick | Controls drone pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right) |
| Power Switch | Turns the drone on/off |
| Return-to-Home (RTH) Button | Initiates the automatic return to the home point |
| Camera Button | Starts/stops recording video or takes photos |
| Mode Switch | Selects different flight modes (Beginner, Sport, etc.) |
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff, hovering, and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. Mastering these maneuvers ensures the safety of your drone and its surroundings.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
Before takeoff, ensure the propellers are clear of obstacles. Level the drone and calibrate the compass if necessary. Gently increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically. Once airborne, maintain a slow, steady ascent.
Stable Hovering
To maintain a stable hover, make small, precise adjustments to the joysticks. Practice maintaining a constant altitude and position. Focus on smooth, controlled movements, avoiding jerky adjustments. Use the drone’s GPS capabilities if available to assist in maintaining position.
Smooth Landing
For a smooth landing, gently lower the drone to the ground, maintaining a slow descent. Reduce the throttle gradually to avoid a sudden drop. Ensure the landing area is clear and level to prevent damage to the drone.
Practice Environment
Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open space, away from people, obstacles, and sensitive areas. Start with short flights, gradually increasing duration and complexity as your skills improve. A large, empty field or park is ideal for practicing.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Once comfortable with takeoff, hovering, and landing, practice basic flight maneuvers. This involves controlling the drone’s movement in all directions and adjusting its altitude and orientation.
Basic Movements
Moving the drone forward, backward, left, and right involves using the right joystick. Forward and backward movements control pitch, while left and right movements control roll. Practice making small, controlled movements to gain a feel for the responsiveness of your drone.
Altitude and Orientation Control
The left joystick controls altitude and yaw (rotation). Increase the throttle to ascend and decrease it to descend. To rotate the drone, gently move the left joystick left or right. Practice smooth transitions between altitude changes and yaw adjustments.
Smooth Turns and Transitions
Smooth turns are achieved by coordinating pitch, roll, and yaw. Avoid abrupt movements, instead using gentle, controlled inputs to make smooth transitions between maneuvers. Practice making turns of varying degrees and speeds.
Sample Flight Plan
A simple flight plan might involve: Takeoff, hover at 10 meters, move forward 20 meters, turn 90 degrees to the right, move right 20 meters, turn 90 degrees to the left, return to the starting point, and land.
Photography and Videography with a Drone
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section will provide tips for optimizing your drone’s camera for stunning visuals.
High-Quality Aerial Shots
To achieve optimal results, maintain a steady flight. Use the drone’s gimbal to stabilize the camera. Avoid flying too close to the subject to prevent blurring.
Camera Settings
Adjusting camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for controlling exposure and depth of field. A lower ISO reduces noise, while a faster shutter speed freezes motion. Experiment with different settings to find what works best for your shooting conditions.
Composition Tips
Use the rule of thirds for balanced compositions. Lead lines and framing techniques can enhance the visual appeal of your shots. Consider the lighting conditions and time of day to optimize your shots.
Creative Aerial Shot Ideas
Here are some creative aerial shot ideas:
- Drone Reveal: Start with a low angle shot and gradually ascend, revealing the landscape.
- Orbital Shot: Circle a subject to showcase its entirety and surroundings.
- Tracking Shot: Follow a moving subject, like a car or person, maintaining a consistent distance.
- Time-lapse: Capture the movement of clouds or traffic over an extended period.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care and maintenance are vital for maximizing flight time and ensuring the longevity of your drone’s battery. This includes understanding charging procedures and recognizing signs of battery failure.
Battery Care and Maintenance
Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries completely. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for storage and usage.
Charging Procedures
Use the manufacturer-recommended charger and power source. Never leave batteries unattended while charging. Monitor the charging process and disconnect the charger once fully charged.
Signs of Battery Failure
Signs of a failing battery include reduced flight time, swelling, leakage, or unusual heating. If you notice any of these signs, replace the battery immediately.
Maximizing Battery Life
Avoid extreme temperatures. Fly in calm conditions to reduce energy consumption. Store batteries at the manufacturer-recommended charge level.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. This includes airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and obtaining necessary permits.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Research the specific laws and regulations in your area governing drone operation. These laws vary by country and region. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines or legal action.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from takeoff and landing to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and its implications.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Avoid flying near airports, military bases, or other restricted airspace. Many countries have designated no-fly zones, often near critical infrastructure or sensitive locations. Check the airspace before each flight using apps like AirMap or B4UFLY.
Drone Registration and Permits
In many jurisdictions, registering your drone and obtaining necessary permits are mandatory. The specific requirements vary, so consult your local aviation authority for detailed information.
Pre-Flight Legal Checklist
Before each flight, review this checklist:
- Check local drone laws and regulations.
- Verify airspace restrictions and no-fly zones.
- Ensure your drone is registered if required.
- Obtain necessary permits or authorizations.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: How To Operate A Drone
Knowing how to troubleshoot common drone problems can save time and prevent frustration. This section will cover common issues, their causes, and solutions.
Common Drone Problems

Common problems include GPS signal loss, low battery warnings, and motor failures. These issues can stem from various causes, including environmental factors, operator error, or mechanical problems.
Troubleshooting Steps
The following table Artikels common problems, their causes, and solutions:
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructed GPS signal, interference, or low satellite visibility | Fly in an open area with clear sky visibility; ensure GPS is enabled; recalibrate the compass |
| Low Battery Warning | Low battery charge, faulty battery, or excessive power consumption | Charge the battery; replace the battery if faulty; reduce flight duration or reduce power consumption |
| Motor Failure | Mechanical failure, overheating, or obstruction | Inspect the motor for damage; allow the motor to cool down; remove any obstructions |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. This guide has provided a comprehensive framework, from pre-flight preparation and control mastery to advanced techniques in aerial photography and troubleshooting. By diligently following the safety procedures Artikeld and practicing consistently in a controlled environment, you can confidently navigate the skies, capture stunning visuals, and responsibly enjoy the thrill of drone flight.
Remember, continuous learning and adherence to regulations are key to a safe and rewarding drone piloting experience.
Popular Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functionality.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibrate your drone before each flight session for optimal performance and accuracy. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, carefully guide the drone back visually, prioritizing safety.
How do I clean my drone’s propellers?
Gently clean propellers with a soft brush and avoid harsh chemicals. Inspect for damage after each flight.
